Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease that cannot be completely cured. The disease requires symptomatic therapy to reduce the severity of the manifestations and improve well-being. Psoriasis on the hands is a frequent site of pathology. It begins with the appearance of small plaques and can progress without proper treatment.
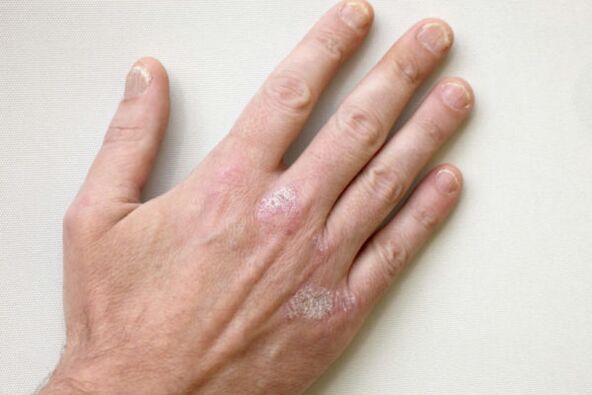
Causes and mechanism of development.
Psoriatic plaques on the hands, particularly the fingers, significantly affect quality of life. Despite the fact that the disease is not contagious, the strange skin defects are alarming. Psoriasis is not the most pleasant disease, and not only because of what it seems, but also because of the risk of complications.
The exact etiology of the appearance of this dermatological disease has not been clarified. Experts identify risk factors that can affect the development of pathology. It is known that psoriasis is not transmitted by contact, it cannot be infected by contact with the patient.
It is also important that it cannot be completely cured, therefore, throughout life, a person is forced to take supportive agents and carefully monitor the condition of the skin at different times of the year. Frequent exacerbations occur in spring and winter. Scientists include the following factors in the development of the disease:
- genetic predisposition;
- immunodeficiencies, a decrease in the protective function of the body;
- frequent skin lesions of viral, fungal, bacterial origin;
- a sharp change in weather conditions;
- chronic skin diseases, including congenital anomalies;
- long-term use of certain medications, particularly anticonvulsants, antidepressants, and steroid hormones;
- psycho-emotional overload;
- metabolic disorders in the body.
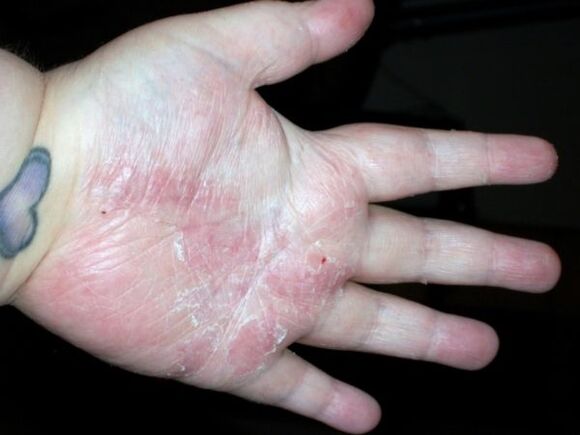
Psoriatic plaques on the hands begin to appear in the area of the small joints, between the fingers, near the phalanges. Pathological elements are most visible on the surface of the palms. It is more difficult to treat psoriasis of such a location, because the hands are often in contact with household chemicals and other irritants.
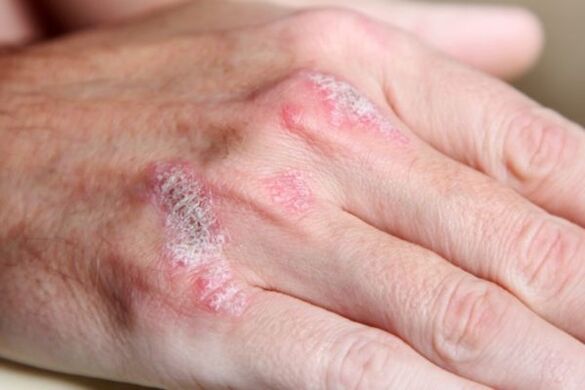
At-risk group
The risk group for developing the disease includes men and women who often face other dermatological diseases. The probability of the disease increases when there have already been cases of psoriasis in the family.
Pathology can occur in people with weakened immunity, in those who live in unsatisfactory living conditions. The risk group also includes those who, due to their activities, are forced to come into contact with aggressive chemicals.
Clinical manifestations
The first signs in the initial stage of the disease will be unique pathological elements in the area of the hands. Plaques may appear on the hands, fingers, and the backs of the palms. If the nails are involved in the pathological process, there is a risk of loss of sensitivity and the appearance of tissue edema.
Increased dryness of the skin causes cracks in the palms. There are signs of thickening of the epidermis, which resembles corns.
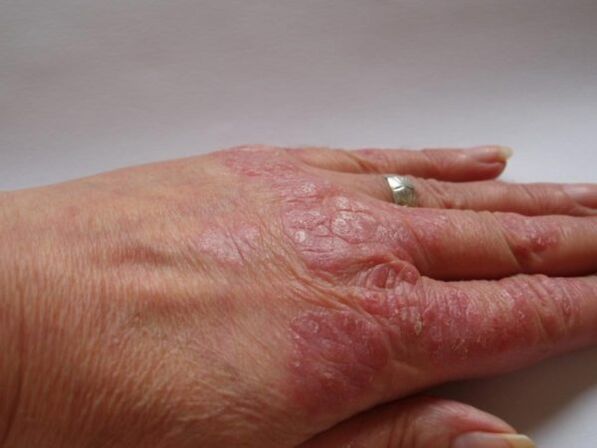
The main manifestations of psoriasis on the hands will be:
- increased dryness, pronounced redness of the skin;
- thickening of the epidermis, increased volume of the fingers due to edema;
- Cracking when the plate cracks
- sometimes there is a fusion of several elements that damage healthy skin.
In winter and autumn, when cold days prevail, the disease manifests itself as intense peeling of the skin. Without treatment, there is a possibility of scratching the hands with infection, then the symptoms are complemented by signs of inflammation.
Forms of pathology
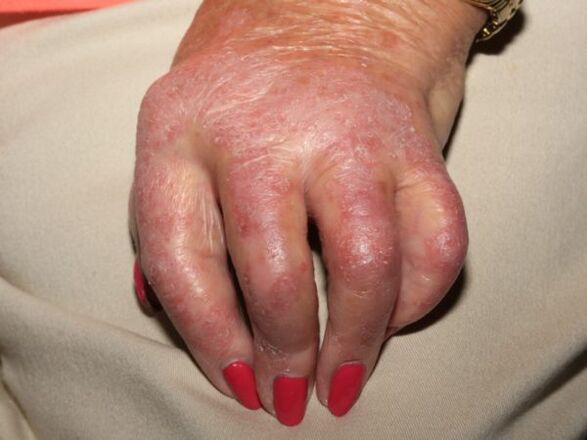
Psoriasis on the hands can take several forms:
- On the fingers. It manifests itself by flaking, the formation of plaques, which are often inflamed. Aggravation occurs in winter. It often leads to complications.
- About brushes. It occurs in 25% of patients, the signs are similar to psoriasis on the fingers, while the skin in the affected area becomes rough, areas of redness appear. The patient complains of constant discomfort, active scaling, itching.
- Palmo-plantar. It occurs in people who do intense physical work. The soles of the feet and the palms of the hands are affected. Rough skin areas resemble solid calluses and cracks very often appear.
- ArthropathicPsoriasis occurs against the background of joint damage. The elements of the rash are found in the phalanges. In addition to external manifestations, the patient is concerned about joint pain during movement and then at rest.
- Pustular. The palms and soles of the feet are affected. Stress and hormonal pathologies become risk factors. The rash has clear boundaries and pustules appear. The disease is often recurrent and difficult to treat.
Each form of the disease proceeds in three consecutive stages: initial, progressive, and stationary. After one cycle (going through 3 stages), the regression of the disease begins. At this stage, the clinical signs almost completely disappear. Treatment is aimed at prolonging the regressive stage as much as possible, otherwise the disease cycle repeats over and over again.
Differential diagnosis
Psoriasis on the hands is differentiated with pathologies such as lichen planus, Reiter's disease, syphilis, seborrheic and atopic dermatitis.
The hallmark of psoriasis during the examination will be the psoriatic triad, by whose presence the doctor can diagnose. It includes the phenomena of stearin stain, dotted bleeding, and terminal film.
Treatment methods
Although psoriasis cannot be completely eliminated, it must be treated to avoid complications and improve quality of life.
The main treatment measures for psoriasis on the hands:
- the use of care products to hydrate and soften the skin;
- taking antihistamines to relieve itching;
- take medications to boost immunity;
- additional use of homeopathic remedies.
For psoriatic lesions, physical therapy and photochemotherapy may be prescribed. When psoriasis is accompanied by diseases of the joints, painkillers from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
Depending on the stage of the disease, the dermatologist will prescribe local anti-inflammatory drugs. It can be salicylic, ichthyol, sulfur tar ointments. To quickly relieve symptoms with severe itching, hormonal ointments can be used; They cannot be used without the permission of the doctor.
To soften and hydrate, you can use baby creams for sensitive skin, which contain herbal ingredients.
Prevention measures
General preventive measures to prevent exacerbations of psoriasis in the hands:
- the use of rubber gloves when cleaning the house when you need to come in contact with detergents and cleaning agents;
- rejection of bad habits, good sleep and balanced nutrition;
- daily care of the skin of the hands using natural cosmetics or pharmaceutical preparations;
- sunbathe regularly, ventilate frequently at home, walk outdoors, avoid stress;
- treat the skin with an antiseptic in case of accidental damage (it is not recommended to bandage the wound for a long time);
- adherence to the Pegano diet, which involves limiting meat dishes, sweets and adding more cereals, vegetables and herbs to the diet.
Prognosis of the disease
The unpleasant psoriatic rash on the hands is causing stress for many patients. At the same time, the experiences only aggravate the situation. Psoriasis can be in regression for a long time, but for this you must follow the therapeutic and preventive measures prescribed by the doctor.
It is impossible to completely get rid of psoriasis, but proper skin care, adherence to a diet and the use of special creams will hide the symptoms of the disease as much as possible. Regardless of the manifestations of the disease, it is recommended to visit a dermatologist every few months to monitor the dynamics of the disease and correct the treatment regimen, if the condition requires it.























